What is an implementation team?
Implementation teams are working groups that promote the implementation and sustainment of psychosocial interventions and operating models in a wellbeing services county or another organisation that provides interventions.
Implementation teams have been identified as an important factor in the successful implementation of interventions. With their help, an intervention is more likely to become well-established as part of the organisation’s services and practices. Teams have also been found to significantly reduce the time required for implementation and establishment.

Implementation team model
On this page, we present the implementation team model, which is a way to organise the implementation of psychosocial interventions aimed at children, adolescents and families in social services and healthcare. The model is based on research literature and has been developed in partnership between Itla and experts working in the wellbeing services counties.
The research literature identifies implementation teams at different levels, ranging from local implementation to decision-making related to national policy. The model, which is a good fit with the structure of the Finnish service system, includes a proposal for implementation teams in wellbeing services counties and collaborative areas and at the national level.
In the model, implementation teams operate within the framework of legislation and national programmes. The operations of the teams are also influenced by facilitating practices, such as management, guidelines, resources and common operating practices.
Teams have different tasks related to decision-making and th more concrete execution of implementation. However, different implementation teams have the same goal: the successful implementation and establishment of psychosocial interventions.
Figure: The implementation team model for the implementation of psychosocial interventions in social services and healthcare

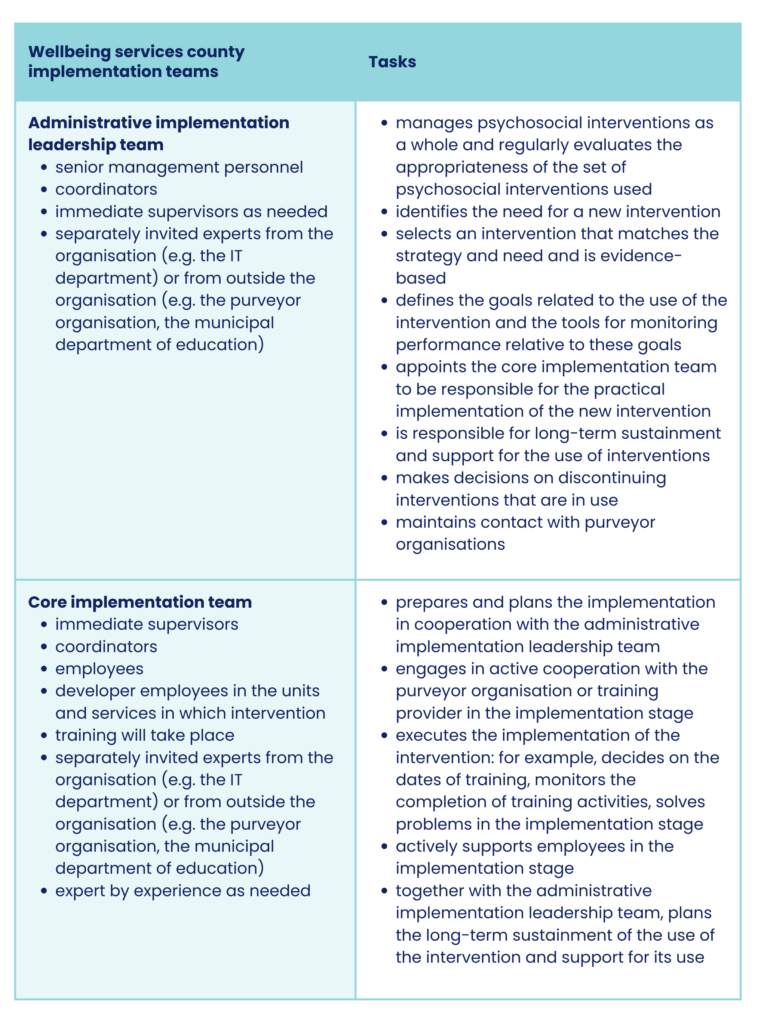
Wellbeing services county implementation teams
In the implementation team model, each wellbeing services county has two kinds of implementation teams: administrative implementation leadership teams and core implementation teams.
The administrative implementation leadership team is the wellbeing services county’s permanent team, which is responsible for management, decision-making and sustainment related to the use of psychosocial interventions. The team may be a pre-existing administrative leadership team, such as the administrative leadership team in charge of child and family services, or a working group established specifically for the purpose of managing the use of psychosocial interventions. This means that it may not be necessary to establish a new team.
The team can also be a working group that is broader than the wellbeing services county organisation and includes directors from other child and family services, such as education services or non profit associations operating in the region. If new interventions are implemented in student welfare services, for example, it is important to also invite other operators from the school community to participate in the administrative implementation leadership team.
The core implementation team is responsible for the concrete execution of the implementation of the psychosocial intervention. The administrative implementation leadership team initiates the operations of the core implementation team. The team consists of supervisors, developer employees and employees from the units that will be trained in the intervention.
The coordinator works in both teams and facilitates cooperation between them.
Table: Wellbeing services county implementation teams and their tasks
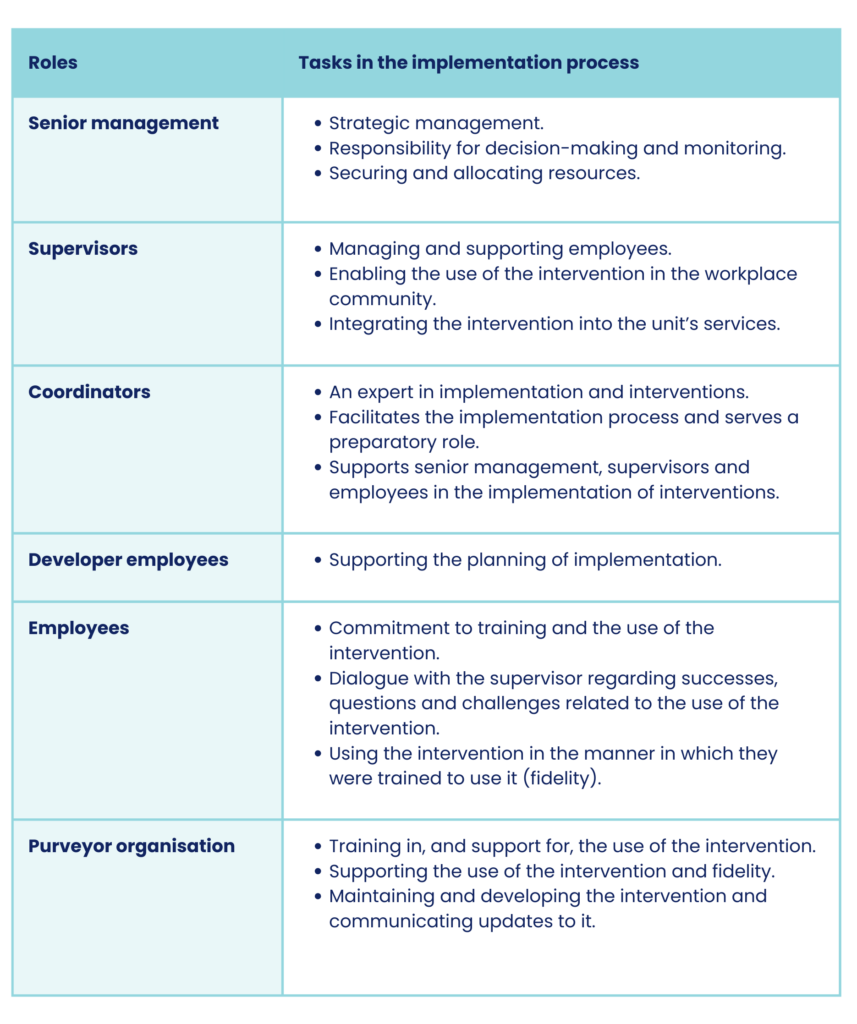
Different roles in the implementation process
Wellbeing services county implementation teams need to have members representing senior management, supervisors and employees. Experts can also be invited to the teams as needed.
The teams need capabilities that are useful in the implementation of psychosocial interventions. Examples of such capabilities include change management, implementation, knowledge-based management, communications, expertise in the intervention and knowledge of the context of use, different professionals’ job descriptions and customers.
Identifying the working group and its various roles and putting them into words is important regardless of how the idea of implementation teams is put into action.
Table: Roles and tasks in the implementation process in a wellbeing services county
Coordinators as providers of support for the implementation and use of interventions
Coordinators are experts with knowledge of psychosocial interventions, implementation, facilitating and their organisation’s service system. Coordinators are tasked with providing their expertise to the administrative implementation leadership team and the core implementation team.
Coordination requires open communication and broad cooperation. In this way, the coordinator, together with both implementation teams, ensures high-quality planning work and the continuity of the use of the interventions.
It is important that the coordinators are the organisation’s own employees who support the systematic implementation and use of different interventions in the organisation, and do not represent or promote the implementation of any single intervention or operating model. The task of the coordinators is not to provide training in interventions, but rather to create the opportunity for interventions to become well-established in the services in cooperation with the management and employees.
In our model, the coordinators have a permanent expert role, which enables long-term support for the implementation processes of interventions and the sustainment of their use. The permanent expert accumulates knowledge from different implementation processes, which can always be subsequently utilised in connection with the implementation of other interventions.

The coordinator’s tasks
- Act as an expert in systematic implementation.
- In cooperation with the management, build a systematic process for the implementation of psychosocial interventions and operating models.
- Support senior management, supervisors and employees in the different stages of the implementation process.
- Actively maintains contact with various operators in the organisation and, if necessary, with operators in the collaborative area and at the national level.
- Facilitates the implementation process by preparing and convening meetings, development events and workshops.
- Compiles and produces information that is important for the execution of the various stages of the implementation process.
- Maintains contact with purveyor organisations and training providers.
Collaborative area implementation teams
In addition to the wellbeing services county level, there should be responsibilities and tasks related to the implementation of interventions in collaborative areas and at the national level. Implementation teams operating at different levels need to cooperate and discuss decisions and their impacts on services as a whole.
The organisation of social services and healthcare in a wellbeing services county also requires cooperation concerning the assessment and sustainment of interventions with other wellbeing services counties in the collaborative area and the university hospital.
The collaborative area implementation team shown in the model consists of experts from the university hospital and representatives of the wellbeing services counties. Cooperation related to psychosocial interventions is also based on cooperation agreements.
In cooperation at the collaborative area level, it is also necessary to take into account the assessment and coordination of interventions used in social welfare services.
National implementation team
In order to be successful, national programme-level implementations require a national implementation team that monitors and supports the progress of implementation.
The national team should have representation from the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, the collaborative areas, the National Institute for Health and Welfare and other parties involved in the use of national programmes or interventions, such as the Council for Choices in Health Care in Finland.
National dialogue helps to improve guidelines, assess the need for resources nationally and regionally, and monitor the achievement of nationally uniform goals related to the use of interventions.
Key things to keep in mind about the implementation team model
- At the core of implementation teams is high-quality, systematic and multi-perspective cooperation between different roles and operators.
- Implementation teams promote systematic cooperation, the execution of a systematic implementation process for interventions, and making interventions well-established in services.
- The team structure helps to clarify responsibilities related to the implementation and use of interventions
- Coordinators support both management and employees in the change related to the implementation process
- Wellbeing services county implementation teams:
- An administrative implementation leadership team that makes decisions and manages interventions as a whole.
- A core implementation team responsible for carrying out the implementation of the new intervention.
- The work of wellbeing services county implementation teams is supported by:
- The collaborative area implementation team
- The national implementation team
Hasson, H. & von Thiele Schwarz, U. 2023. Implementeringsboken: så inför du nytt som gör nytta.
Metz, A., Bartley, L. (2020). Implementation Teams: A Stakeholder View of Leading and Sustaining Change. In: Albers, B., Shlonsky, A., Mildon, R. (eds) Implementation Science 3.0. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03874-8_8
Psychological interventions implementation manual: integrating evidence-based psychological interventions into existing services. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2024. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
cNIRN, 2023. Implementation Teams Overview. Implementation Teams Overview (Module 3) – AI Hub (unc.edu).
